|
Cancer - Kidney(구연)
|
(E-087)
|
|
|
머신러닝을 이용한 신장암 재발 예측 알고리즘 |
| 가톨릭대학교 의과대학 의료정보학교실, 1 가톨릭대학교 의과대학 서울성모병원 비뇨의학과 |
| 김형민, 이선정, 박소진, 최인영, 홍성후1 |
Purpose: RCC (Renal Cell Carcinoma) has a high recurrence rate of 20% to 40% after nephrectomy for clinically localized disease. Therefore, regular monitoring and constant management are very important.
The purpose of this study is to develop an algorithm that predicts the probability of recurrence within 5 and 10 years of RCC. The developed algorithm will helps determine the personalized treatment strategies for RCC patients after surgery.
Materials and Methods: A total number of 6,849 Korean RCC patient data were collected from 8 tertiary care hospitals in the KORCC (KOrean Renal Cell Carcinoma) web-based DB. To predict RCC recurrence, we extracted 2,814 analytic data from the KORCC web-based DB and divided the data randomly into 80% train and 20% test. We used 8 machine learning algorithms to predict the probability of RCC recurrence and compared those results.
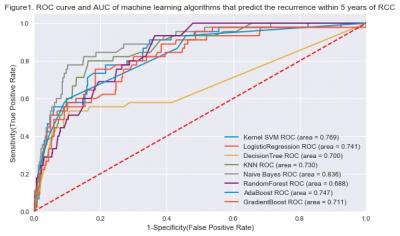
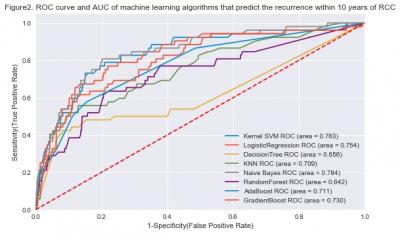
Results: Figure 1 and Figure 2 shows the ROC curve and AUC (Area Under the Curve) of prediction algorithms. Within 5 years of surgery, the highest AUC was Naives Bayes model, and the value was 0.836. Within 10 years of surgery, The highest AUC was Naives Bayes model, and the value was 0.784. We finally developed RCC recurrence prediction algorithm using naive bayes model with the highest AUC value.
Conclusion: We developed an algorithm that predicts the probability of RCC recurrence within 5 and 10 years using KORCC DB, a large-scale RCC cohort in Korea. It is expected that developing this algorithm as a system will help clinicians to determine the personalized treatment strategies for RCC patients after surger |
  |
|
keywords : renal cell carcinoma, recurrence, machine learning |
|

