|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-064)
|
|
|
상부요로상피암에서 로봇도움하 체내외 방광소매절제술의 비교 |
| 분당서울대학교병원 비뇨의학과 |
| 송상헌, 예창희, 이상철, 홍성규, 변석수, 이상은, 오종진 |
Purpose
To evaluate a single institution experience of complete intracorporeal bladder cuffing and distal ureter excision in robotic radical nephrouretectomy (RNU) for upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC).
Materials and Methods
168 patients treated for UTUC with robotic RNU at our institution from May 2009 to October 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. 92 patients underwent complete intracorporeal excision of the distal ureter and bladder cuff after robotic dock repositioning, and 76 patients were converted to an extracorporeal approach via Gibson incision after robotic RNU. Perioperative outcomes including operation time, estimated blood loss (EBL), transfusion rates, use of painkillers, Visual analogue scale (VAS) pain scores, and complication rates were compared, as well as pathological and oncological outcomes. Uni- and multi-variate Cox regression models were performed to find significance of surgical approach to survival.
Results
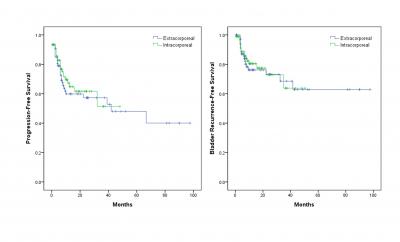
Mean and median follow-up duration for intracorporeal excision patients were 30.8 months and 27.8 months, respectively, compared to 45.5 months and 38.6 months in extracorporeal approach patients. There were no significant differences in baseline patient characteristics between the two groups. Patients who underwent intracorporeal bladder cuffing had less EBL (169.8±150.4 vs 214.6±157.0, p=0.091) and decreased pain at 1 week (VAS score 1.18±1.1 vs. 2.2±1.1, p=0.017). Pathological outcomes including margin positivity was not significantly different, and oncological outcomes including local and intravesical recurrence, cancer specific mortality, and overall mortality were comparable to patients who received extracorporeal bladder cuffing. Intracorporeal bladder cuffing was not associated with increased risk of progression on univariate analysis (HR 0.600, 95% CI 0.314-1.147; p=0.122).
Conclusion
Based on our experience, intracorporeal ureteral resection and bladder cuffing can be a safe and oncologically non-inferior alternative |
 |
|
keywords : Intracorporeal cuffing, nephrouretectomy, upper tract urothelial carcinoma |
|

