|
Cancer - Prostate(구연)
|
(E-140)
|
|
|
Complementing the Active Surveillance Criteria for Prostate Cancer with Multi-parametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| Department of Urology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital |
| Won Hoon Song, Dan Bee Lee, Seung Ryong Baek, Seung Soo Lee, Jong Kil Nam, Sung-Woo Park |
Objectives; To evaluate the usefulness of multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) to avoid misclassification of patients with clinically significant prostate cancer (PCa) into active surveillance (AS).
Materials and Methods; Patients with Gleason grade group (GG) 1 PCa on systematic biopsy who underwent mpMRI before radical prostatectomy (RP) were included. mpMRI and pathological results were compared between the AS and NOT-AS candidates. Unfavorable disease was defined by T3-4 or GG upgrade at RP specimen. We established an ideal cut-off of Prostate Imaging-Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) score for predicting unfavorable disease, and analyzed a location of index lesion on mpMRI.
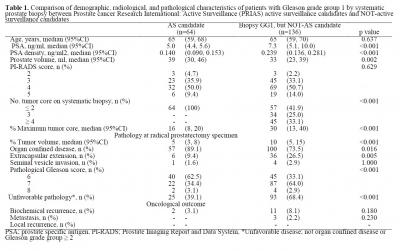
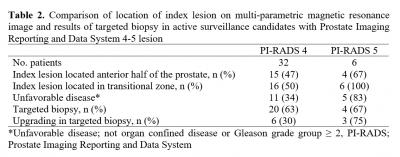
Results; PI-RADS scores were not different between AS candidates (n=64) and NOT-AS candidates (n=136) (p=0.629).(Table 1) The rate of unfavorable disease was greater for patients with a PI-RADS score 5 (83.3%) than those with a score ≤4 (34.5%; p=0.030). Moreover, most PI-RADS 5 lesion in AS candidates were located in the anterior half of the prostate, with a GG upgrading on targeted biopsy in 75% cases.(Table 2)
Conclusions; Among the patients with GG 1 PCa, PI-RADS scores were not different between AS and NOT-AS candidates. Nonetheless, AS candidates with PI-RADS 5 lesion were diagnosed with unfavorable disease in >80% RP specimens. Significant cancer located in the anterior half of the prostate including the transitional zone can be missed by systematic biopsy.
|
  |
|
keywords : Active surveillance, Magnetic resonance imaging, Prostate biopsy |
|

