|
Cancer - Kidney(구연)
|
(E-089)
|
|
|
고도 복잡성 신종양에서 신장전체절제술과 신장부분절제술 후 재발: 성향점수매칭 연구 |
| 분당서울대학교병원 비뇨의학과, 서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학교실 |
| 김환익, 김정권, 예창희, 최준혁, 이학민, 오종진, 이상철, 홍성규, 변석수 |
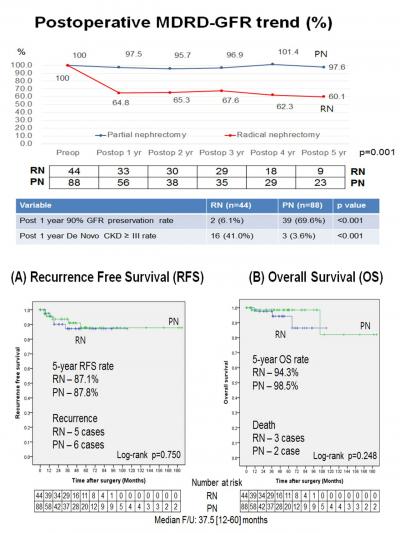
Obejective: We evaluated recurrence after radical and partial nephrectomy in patients with High complex renal tumor of RENAL Nephrometry score (RNS) ≥10.
Materials and Methods: A total of 474 patients (Radical nephrectomy (RN, n=236) vs Partial nephrectomy (PN, n=238) from December 2003 to December 2019 in single tertiary referral center were included in the study. Renal functional outcomes defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) changes, recurrence pattern, and recurrence free survival (RFS), overall survival (OS) were assessed using propensity score matched analysis. Predictors of recurrence and death were evaluated with Cox-regression analysis
Results: After propensity score matching, 44 cases in RN group and 88 cases in PN group were matched with no significant difference of preoperative clinical factor. Patients with PN had significantly higher renal function preservation rate (p<0.001). There were 5 recurrences in patients with RN and 6 in patients with PN, respectively. Patients with PN had higher 5-year RFS rate (87.8%) and OS rate (98.5%) than patients with RN (RFS: 87.1% (p=0.750), OS: 94.3% (p=0.117)) without significance. Patients with Body mass index (BMI) ≥23 had lower 5-year RFS rate (85.5%) and OS rate (95.6%) than patients with BMI<23 (RFS: 90.0% (p=0.195), OS: 100% (p=0.117)) without significance. Significant predictors for recurrence were tumor size (HR=1.094[1.001-1.196 p=0.047) and clinical T stage (p=0.025). Significant predictors for death were R portion in RNS (HR=3.80 [1.03-14.11], p=0.046).
Conclusions: In RNS ≥10, PN could be considered to preserve renal function if technically feasible. Nevertheless, PN needs to be done with prudent caution in some patients due to higher potential for recurrence and poor survival. |
 |
|
keywords : Recurrence, High complex renal tumor, Renal cell carcinoma |
|

