|
Cancer - Prostate(구연)
|
(E-144)
|
|
|
저-중등도 위험 전립선암에서 PI-RADS 4점과 5점 병변은 생화학적 재발의 위험인자이다. |
| 부산대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학교실¹ |
| 김경환¹, 박지훈¹, 강병진¹, 박시균¹, 이권경¹, 구자윤¹, 하홍구¹ |
Objectives
The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between PI-RADS 4-5 lesions on multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) and biochemical recurrence (BCR) after prostatectomy in the low-intermediate risk prostate cancer patients.
Materials & Methods
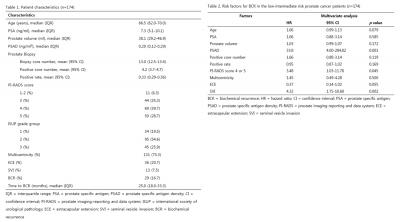
Out of 231 prostate cancer patients who underwent mpMRI scan and radical prostatectomy in our institute from Aug, 2016 to Feb, 2019, we identified 174 cases with low-intermediate risk. Patients with Gleason score ≤ 7 and prostate specific antigen (PSA) ≤ 20 ng/ml were classified as low-intermediate risk prostate cancer group. BCR was defined as PSA ≥ 0.2 ng/ml with a second confirmatory laboratory value. Cox proportional hazard analysis and Kaplan-Meier analysis were performed.
Results
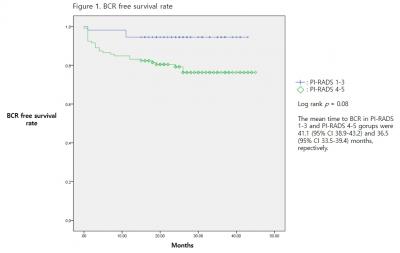
BCR developed in 29 (16.7%) patients at a median follow-up of 28.0 months. Median of age, PSA and PSA density (PSAD) were 66.5 years, 7.3 ng/ml and 0.20 ng/ml2, respectively. PI-RADS 1-2, 3, 4 and 5 index lesions were observed in 11 (6.3%), 44 (25.3), 69 (39.7%) and 50 (28.7%) patients, respectively. In Cox proportional hazard model, PI-RADS 4-5 lesions were significant risk factors for BCR (p = 0.045) along with PSAD and seminal vesicle invasion. BCR free survival rate was significantly lower in PI-RADS ≥ 4 group than PI-RADS ≤ 3 group (log rank p value = 0.08). Mean time to BCR in PI-RADS ≥ 4 and PI-RADS ≤ 3 patients were 36.5 and 41.1 months, respectively.
Conclusion
PI-RADS 4 and 5 lesions on preoperative mpMRI were identified as significant predictors for BCR in the low-intermediate risk prostate cancer patients.
|
  |
|
keywords : Biochemical recurrence, PI-RADS score, Prostate cancer |
|

