|
Cancer - Kidney(구연)
|
(E-093)
|
|
|
신문부 종양과 비 신문부 종양에 대해 로봇을 이용한 복강경하 부분 신 절제술 후 결과 비교 |
| 성균관대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실 |
| 유현수, 강민용, 성현환, 전황균, 정병창, 전성수, 이현무, 서성일 |
Background: We evaluated the characteristics of renal hilar tumors and compared peri- and postoperative functional outcomes of patients with hilar and nonhilar tumors.
Materials and Methods: we retrospectively reviewed the records of 1,012 patients who underwent RPN at our center from 2008 to 2018. A total of 1,004 patients were included for analysis: 135 patients with a hilar tumor and 869 patients with a nonhilar tumor. We performed a 1:2 propensity score matching analysis and patients were stratified into those with hilar lesions (135 patients) and those with nonhilar renal lesions (270 patients). Preoperative variables, perioperative outcomes and pathologic outcomes compared between hilar and nonhilar groups.
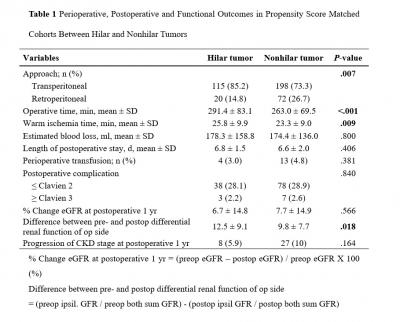
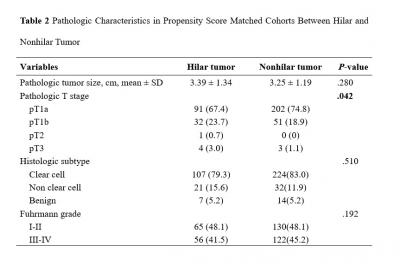
Results: Preoperative tumor size and tumor location which showed low P-value were selected as matching variables for propensity score matching analysis. Hilar tumors were more likely to be associated with the transperitoneal approach (P =0.007), longer op time (P < 0.001), longer WIT (P =0.009) and greater reduction in difference between pre- and preoperative differential renal function of op side (P = 0.018). There were no significant differences in EBL, length of postoperative hospital stay, transfusion rate, perioperative complication rate, percent change of eGFR at postoperative 1 year. And hilar tumors tended to have more pT1b tumors and pT3a upstaging (P = 0.042).
Conclusion: Hilar renal tumors should be considered for robotic PN as they do not show more complications or adverse events.
|
  |
|
keywords : Hilar tumor, Robotic partial nephrectomy, Outcomes |
|

