|
Basic Research - Infertility & Sexual Dysfunction(구연)
|
(E-020)
|
|
|
쥐모델에서의 미세먼지와 불임과의 관계 |
| 비뇨의학과 |
| 태범식, 김연주, 전병조, 이영훈, 유정완, 최훈, 박재영, 배재현 |
Background: Exposure to urban particulate matter (PM) has been linked to aggravation of various health problems in Korea. Although the effects of PM on the respiratory tract have been extensively studied, there were few studies about impact of PM on the urologic disease including study about infertility. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the correlation between PM exposure and infertility based on a rat experimental model.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley (SD, 6weeks) rats were used to establish animal models with PM exposure once a day for six weeks. Sperm quality, epididymal morphology, expressions of inflammatory markers, and expression in testicular tissues, and expressions of BTB junction proteins were detected.
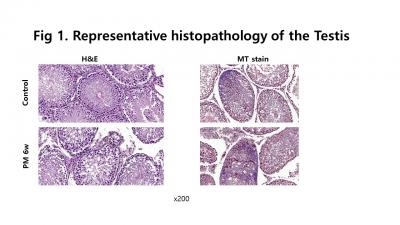
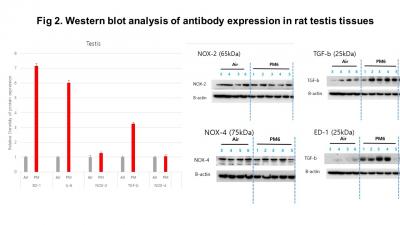
Result: There weas significant difference between control group and PM exposure groups in sperm Motility (10.94 ± 5.93% vs 7.20 ± 3.95%, p=0.021) and proportion of normal shape of sperm (Normal shape: 13.07 ± 6.18% vs 7.04 ± 1.68 %, p=0.013). However, there was no significant difference between tow groups in sperm concentration (6.69 ± 3.30 x 106 vs 7.56 ± 1.66 x 106, p=0.278). In immunohistochemical staining in testicular tissues, Seminal tubules tissue sections with HE staining of rats were different compared to PM group. The expression of the proteins including NOX-2, NOX-4, TGF-b, ED-1 and IL-6 were significantly increased and the spatial arrangement of b-actin was completely disordered through Immunofluorescence and Western blots tests.
Conclusion: This result suggests that PM2.5 exposure may engenders male reproductive function injury.
|
  |
|
keywords : particulate matter, Infertility, Rat |
|

