|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-049)
|
|
|
여성 로봇 근치적 방광 절제술의 종양학적 결과: 남성 로봇 근치적 방광 절제술과의 비교 |
| 1고려대학교 안암병원, 2경북대학교병원, 3경희의료원, 4양산부산대학교병원, 5인제대학교 부산백병원, 6성균관의대 삼성서울병원, 7서울대학교병원, 8가톨릭대학교 서울성모병원, 9연세의대 신촌세브란스병원, 10한림대학교 강남성심병원, 11한양대학교병원 |
| 진현중1, 심지성1, 권태균2, 김태환2, 전승현3, 이상협3, 강성구1, 남종길4, 김완석5, 정병창6, 오종진7, 이상철7, 이지열8, 홍성후8, 나군호9, 한웅규9, 함원식9, 이영구10, 이용성10, 박성열11, 윤영은11, 강석호1, 구자현7; Korean Robot Assisted Radical Cystectomy (KORARC) Study Group |
|
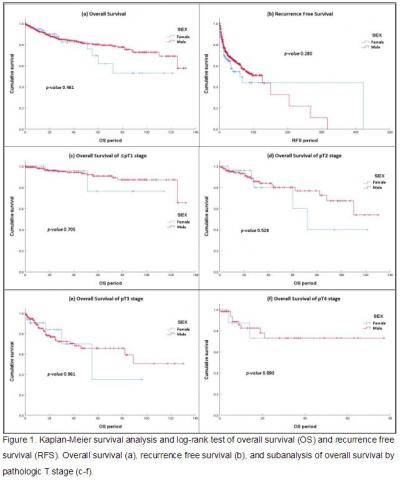
Women are less likely to develop bladder cancer than men, but female bladder cancer is related to advanced clinical presentation and unfavorable outcome. This study aimed to investigate the gender difference in bladder cancer with robotic radical cystectomy. Patients who had robotic radical cystectomy from 2007 to 2019 were included in this multicenter retrosepctive cohort study. The 749 patients were categorized into two groups; female (n=111) and male (n=638). We compared the perioperative and oncological outcomes between two groups. The pre-radical cystectomy treatment (TURBT, intravesical therapy, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, partial cystectomy) and initial clinical stage were no different between two groups. We found that female patients had higher rate of blood transfusion (25.5% vs. 14.7%; p=0.005) and ileal conduit pouch reconstruction (50.5% vs. 37.6%; p=0.028), and lower rate of nerve sparing (14.5% vs. 45.8%; p<0.001) compared to male patients. Other intraoperative indicators (open conversion rate, corporeal type, lymph node dissection region, operation time, estimated blood loss, etc.) were not significantly different between two groups. The pathologic T and N stage of female bladder cancer after robotic radical cystectomy were not significantly different from male bladder cancer. On variant histology, female group had more squamous metaplasia than male group (13.5% vs. 6.32%, p=0.010). There was no significant difference in overall survival between female and male by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and log-rank test (p=0.461). The subanalyasis of overall survival by pathologic T stage also supported this result. The recurrence free survival was not statistically different between two groups (p=0.280). In conclusion, in this study, female was not related to poor oncological outcomes in bladder cancer with robotic radical cystectomy. |
 |
|
keywords : Radical cystectomy, female bladder cancer, robotic surgery |
|

