|
Incontinence & Female Urology & Neurourology(구연)
|
(E-178)
|
|
|
초음파 활용 바이오피드백을 이용한 골저근 훈련은 근치적 전립선 수술 후 요자제 회복을 증진시킨다 |
영남대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실¹
영남대학교 의과대학 재활의학 교실² |
| 고영휘, 김영욱,¹ 이동규² |
Purpose
To determine the benefit of pelvic flow muscle exercise (PFME) with visual biofeedback on recovery from incontinence, we investigated variables associated with early return of continence by analyzing the data of patients that underwent robot-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) by a single surgeon, who used the same technique in all patients.
Materials and methods
Of the 100 patients enrolled, 50 consecutive patients completed ultrasonography-guided biofeedback based PFME (the exercise group), and the other 50 consecutive patients right before PFME instructed Kegel exercise right after removal of catheter (the control group). The primary endpoint was variables associated with zero-pad continence regain within 3 months of RARP.
Results
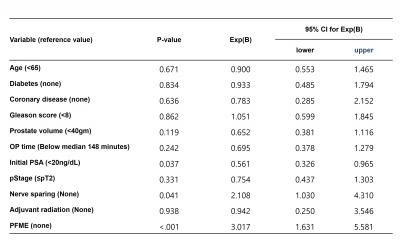
Continence regain percentages (defined as zero-pads per day) at 1, 3, and 6 months after surgery for whole subjects were 47%, 76%, and 94%, respectively. The exercise group achieved significantly higher recovery rates at 1 month (58% vs. 36%, p=.028), 3 months (100% vs. 52%, p<.001), and 6 months (100% vs. 88%, p=.0232), in comparison with the control group. Time to continence recovery was significantly shorter in the exercise group (29.9 vs. 94.8 days, p<.001). Cox regression analysis demonstrated that a nerve sparing procedure (HR=2.108, p=.41), a lower PSA (<20ng/dL, HR=1.781, p=.037), and the implementation of PFME with biofeedback (HR=2.801, p=.001) were independent predictors early recovery from postprostatectomy incontinence (Table). Stratification by age showed those younger than 65 years did not significantly benefit from exercise (log-rank test, p=.08), but that their elderly counterparts, that is, patients aged 65 to 70 years (p=.007) and patients > 70 years old (p=.002) benefited significantly.
Conclusions
This study suggests the postoperative implementation of PFME with biofeedback speeds up recovery of continence after RARP, especially in elderly population. |
 |
|
keywords : Urinary incontinence, Prostatectomy, Biofeedback |
|

