|
Cancer - Kidney(구연)
|
(E-091)
|
|
|
Metabolism을 이용한 신장암의 새로운 표적 치료 가능성 연구 |
¹한양대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학교실
²한양대학교 의생명공학전문대학원 임상의과학과 |
| 이지영¹, 황현지¹·², 홍성휘¹, 장은비¹·², 박성열¹, 문홍상¹, 윤영은¹* |
The glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) is a facilitative membrane glucose transporter. GLUT1 is the most frequently implicated in human cancers and is responsible for augmented glucose uptake and metabolism. However, no studies have been conducted on the role or anticancer effects of GLUT1 in kidney cancer. Therefore, in this study, unlike the previously used treatments for kidney cancer, inhibition of GLUT1 is expected to be able to treat kidney cancer.
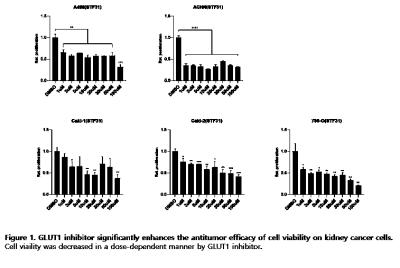
Cell proliferation was measured by EZ-Cytox assay kit. Kidney cancer cell line, A498, ACHN, 786-O, Caki-1 and Caki-2 cells were treated with STF31 dose-dependent manner( 1, 3, 5, 10, 20, 30, 50, and 100uM) for 24hr.
The increase in glucose uptake along with tumor progression is due to an increment of facilitative glucose transports as GLUT1. GLUT1 prevents cell death of cancer cells caused by growth factors deprivation.
So, we first conducted a cell-proliferation assay to confirm the anticancer effect of the GLUT1 inhibitor.
STF-31, a GLUT1 inhibitor, was treated in a dose-dependent manner in kidney cancer cell lines. As a result, it was confirmed that cell proliferation decreased dose-dependent on all cell lines.
GLUT1 inhibitor showed anticancer effect in RCC (Renal cell carcinoma) cell lines. These results suggest a new alternative to kidney cancer treatment. Different from the previously used kidney cancer targeted therapy, to present the possibility of treating kidney cancer with a new approach called energy blocking in cells by inhibiting GLUT1, a major source of energy needed for cancer cell growth and vascular generation. |
 |
|
keywords : RCC, GLUT1, STF-31 |
|

