|
Basic Research - Cancer(구연)
|
(E-018)
|
|
|
The clinical significance and impact on survival of FGFR3, P15 and P16 in urothelial cancer |
Department of Urology, Kyung Hee University, School of Medicine
Department of Pathology, Kyung Hee University, School of Medicine¹ |
| Dong Soo Kim, Seung Hyun Jeon, Sun-Ju Lee, Choong Hyun Lee, Sung-Goo Chang, Ji-Youn Sung¹, Sang Hyub Lee |
Introduction
We studied the clinicopathological significance of FGFR3, P15 and P16 in patients diagnosed with urothelial carcinoma
Material and Methods
225 cases from 1998 to 2012 of patients who underwent surgery for urothelial cancer were collected for analysis. Cases with missing FGFR3, p15 or p16 immunohistochemistry data were excluded and a total of 215 patients were ultimately included. Factors such as patient age, sex, TNM data, overall survival, lymphovascular invasion and perineural invasion were evaluated against immunohistochemistry findings. Univarate and multivariate analysis was done to evaluate factors associated with overall survival.
Results
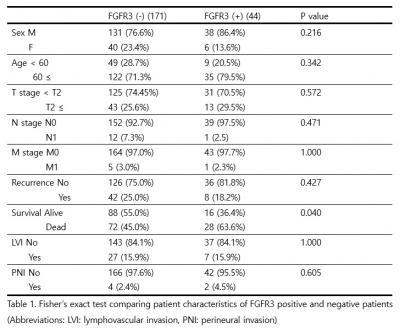
For the sake of evaluation, +3 was considered positive for statistical analysis. Among the 215 patients FGFR3 positive was seen in 44 patients (20.5%), P15 positive in 40 (18.6%) and p16 positive in 39 (18.1%). Fisher’s exact test showed statistical significance between FGFR3 (+) and overall survival (p=0.040). P15 and P16 did not show any clinical relevance with patient factors. Kaplan Meier curve and log rank test, age over 60 (p < 0.005), FGFR3 (+) (p = 0.028), stages T2 or higher (p < 0.005), Lymph node invasion (N1) (p < 0.05), metastasis (M1) at the time of diagnosis, lymphovascular invasion (LVI) (p = 0.048), and perineural invasion (PNI) (p < 0.010) were found to be statistically associate with overall survival. Cox proportional hazard model showed that age over 60, FGFR3 (+), N1 and PNI was associated with lower survival.
Conclusion
FGFR 3 (+) is associated with poorer survival but p15 or p16 did not show statistical significance.
|
 |
|
keywords : Urothelial cancer, FGFR3, P15, P16 |
|

