|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-054)
|
|
|
방광암의 예후 예측용 바이오 마커로서의 Β-hCG, CA19-9, CA125, CEA |
| 서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학교실, 서울대학교병원 비뇨의학과 |
| 육형동, 김승이, 정창욱, 곽철, 김현회, 구자현 |
Objective: We evaluated the prognostic potential of the β-hCG, CA19-9, CA125, and CEA tumor markers for bladder cancer patients who underwent radical cystectomy (RC) for urothelial cancer (UC)
Materials and Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the records of 369 patients who underwent RC with UC from October 2012 until December 2019. Preoperative levels of CA19-9, CA125, CEA, and β-hCG were measured 1-2 days before surgery in all patients. Serum biomarker cutoff values were used as normal and elevated values (CA19-9: 0–37 U / mL; CA125: 0–35 U / mL; CEA: 0–3.8 ng / mL; β-hCG: 5 mIU/mL). The primary and secondary outcome were OS and RFS. Kaplan-Meier analysis and log-rank tests were used to compare the differences between survival rates. Cox proportional regression analysis was used to identify independent predictors of RFS and OS.
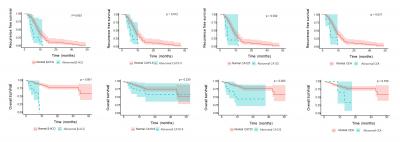
Results: The proportion of abnormal β-hCG, CA19-9, and CA125 was significantly higher in locally advanced bladder UC than in organ-confined bladder UC. In patients with preoperative β-hCG and CA125 abnormality, there was poor prognosis of recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS). Using the Cox multivariate regression analysis, both β-hCG and CA125 were found to be significant independent factors for predicting OS and RFS. In addition, patients with a high number of increased tumor markers showed significantly worse OS and RFS than patients with a low number of increased tumor markers.
Conclusion: Serum β-hCG and CA125 levels could potentially be used for UC prognosis in patients undergoing radical cystectomy. To assess their usefulness in evaluating long-term recurrence and survival, further treatment responses and large-scale additional studies are needed.
|
 |
|
keywords : Biomarker, Bladder cancer, Cancer antigen |
|

