|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-046)
|
|
|
혈뇨 환자에서 방광암 예측을 위한 노모 그램 |
| 서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학교실, 서울대학교병원 비뇨의학과 |
| 육형동, 황영철, 정창욱, 곽철, 김현회, 구자현 |
Objective:
We evaluated risk factors in patients with hematuria and developed a nomogram for the prediction of bladder cancer presence.
Materials and Methods
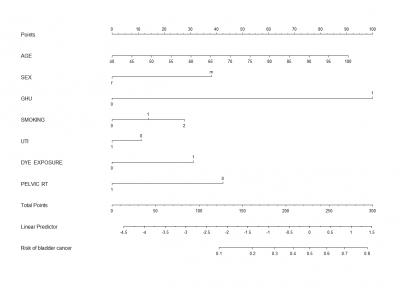
We retrospectively analyzed the records of patients without a history of bladder cancer undergoing initial evaluation for asymptomatic hematuria from October 2008 until March 2020. Clinical risk factors including age, sex, gross hematuria, dysuria, analgesics, cyclophosphamide use, previous urologic surgery, urine cytology, smoking status, urinary tract infection, dye exposure and pelvic radiation therapy were recorded. Logistic regression analysis was performed to identify factors associated with a bladder cancer diagnosis and to develop our model. Receiver operating curves were shown to detect bladder cancer and tested it for its ability to distinguish between real cases.
Results
Of the 1978 patients who presented with asymptomatic hematuria. Increasing age (OR = 1.03, p < 0.001), male (OR = 2.44, p < 0.001), have gross hematuria (OR = 8.17, p < 0.001), have a dye exposure history (OR = 1.95, p < 0.017), and were former and current smokers (OR = 1.15 and 1.76, p < 0.004 were independent predictors of bladder cancer presence. A nomogram created using this model was able to predict risk of a bladder cancer diagnosis with good discrimination (areas under the curve 0.77 95% CI 0.75–0.83).
Conclusion
A nomogram can predict the risk of bladder cancer presence with high accuracy in patients with asymptomatic hematuria.
|
 |
|
keywords : Bladder cancer, Hematuria, Nomogram |
|

