|
Cancer - Prostate(구연)
|
(E-097)
|
|
|
임상적으로 중요한 전립선암의 진단에 있어서 전립선 건강 지수와 PI-RADS 버전 2의 결합 |
| 성균관대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학과교실 |
| 송 완, 정재훈, 강민용, 성현환, 전황균, 정병창, 서성일, 전성수, 이현무 |
Objective: To evaluate the performance of combining prostate health index (PHI) and Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System version 2 (PI-RADSv2) for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer (csPCa).
Methods: Patients who underwent prostate biopsy due to elevated prostate-specific antigen (PSA > 2.5 ng/mL) and/or abnormal digital rectal examination (DRE) were reviewed. Serum markers for PSA, free PSA (fPSA), and [-2] proPSA (p2PSA) were measured, and PHI was calculated as ([p2PSA/fPSA] x [PSA] 1/2). multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) was performed using a 3.0T scanner and scored using PI-RADSv2. csPCa was defined as defined as either grade group [GG] ≥2 disease or GG1 cancer detected in >2 cores or >50% of positive on biopsy. Univariable and multivariable logistic regression modelling, along with receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to predict csPCa
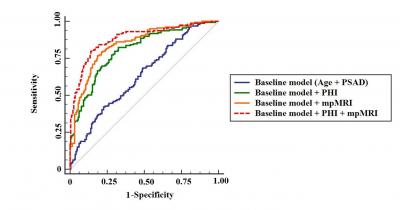
Results: Of the total 358 patients, 159 (44.4%) were diagnosed with csPCa. On univariable analysis, age, PSA density (PSAD), PHI and PI-RADSv2 were associated with csPCa. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of baseline model incorporating age and PSAD was 0.663. The AUC of combining PHI and PI-RADSv2 to baseline model was greater than that of PHI alone to baseline model (0.884 vs. 0.807, P < 0.0001) and PI-RADSv2 alone to baseline model (0.884 vs. 0.846, P = 0.0002). If biopsy was restricted to patients with PI-RADS 5 as well as PI-RADS 3 or 4 and PHI ≥ 25, 33.2% of unnecessary biopsy could be avoided at the cost of missing 8.2% of csPCa.
Conclusions: The combination of PHI and PI-RADSv2 to baseline model incorporating age and PSAD had higher accuracy for detection of csPCa compared with PHI or PI-RADSv2 alone
|
 |
|
keywords : Prostate cancer, Prostate health index, PI-RADS version 2 |
|

