|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-070)
|
|
|
비근침윤 방광암에서 지속적 방광 세척과 방광내 항암요법이 암재발에 미치는 영향 비교 |
| 연세의대 강남세브란스병원 비뇨의학과, ¹순천향의대 순천향대학교병원 비뇨의학과 |
| 김종원, 김도경¹, 안현규, 하지수, 이돈구, 고종철, 조강수 |
Postoperative intravesical chemotherapy (IVC) is recommended to prevent the recurrence of cancer in patient who have low or intermediate risk bladder cancer. However, it has potential complications. Therefore, continuous bladder irrigation (CBI) is considered as an alternative. We performed a systematic review to confirm the efficacy of CBI compared with IVC after transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC).
We systematically searched the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases to identify studies that assessed the difference in recurrence of cancer between those who underwent CBI after TURBT and those who underwent IVC after TURBT. Data were pooled using a random effects model. And a meta-analysis was performed.
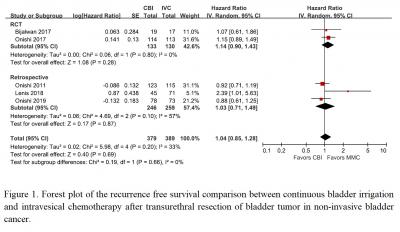
Overall 5 trials (379 cases with CBI, 389 cases with IVC) were considered suitable for meta-analysis. There was no significant difference of recurrence-free survival between two groups (hazard ratio, 1.04; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.85-1.28; p = 0.69)(Fig.1). And the risk of tumor progression was similar between two groups (odd ratio [OR], 0.71; 95% CI, 0.40-1.27; p = 0.25). On the other hand, CBI group had fewer complications than IVC group (OR, 0.17; 95% CI, 0.09-0.31; p < 0.00001).
In conclusion, CBI provided the similar efficacy for cancer recurrence and fewer complications compared with IVC. It suggests CBI may be an alternative of IVC to those who had NMIBC for prevention of the cancer recurrence.
|
 |
|
keywords : Bladder cancer, Intravesical chemotherapy, Irrigation |
|

