|
Cancer - Prostate(구연)
|
(E-099)
|
|
|
75세 이상 노인에서 비전이성 전립선암에 대한 로봇이용 근치적 전립선 적출술과 방사선 치료의 생존율 비교: 다기관연구 |
영남대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실, 영남대학교병원
서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실, 분당서울대학교병원,
국립암센터 비뇨의학 교실
가톨릭 대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실, 가톨릭대학교 서울성모병원
부산대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실, 양산부산대학교병원
성균관대 의과대학 비뇨의학교실, 성균관의대 삼성서울병원,
서울대학교 의과대학 비뇨의학 교실, 서울대학교병원 |
| 고영휘, 변석수, 정재영, 하유신, 박성우, 전성수, 곽철 |
Purpose: To investigate the overall survival (OS) and cancer-specific survival (CSS) after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) in comparison with radiation therapy (RT) which has long been the recommended modality in elderly patients (≥75 years) with non-metastatic prostate cancer (PCa), given contemporary reported life span of 79.3 years (2017).
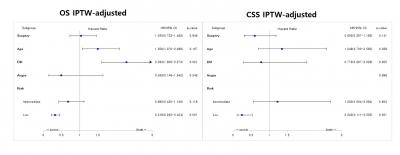
Materials and Methods: Retrospective data were constructed from 7 tertieray hospitals across South Korea in which patients aged over 75 years were managed by RARP or RT for localized/locally advanced PCa. To account for indication bias, an inverse probability of treatment-weighting (IPTW) was applied based on age and the risk stratification of PCa, then IPTW unadjusted and adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression modeling was performed.
Results: Data revealed 1,110 patients with RARP (n=883) or RT (n=227). During mean followup of 74.45months, OS (91.9% vs. 91.0%) and CSS (97.8% vs. 98.0%) between each group were similar. After IPTW, 5-years OS and OSS was significantly higher in RT than RARP group only in the patient aged over 80 years (97.8% vs. 90.7% for OS, 100% vs. 96% for CSS) and low risk stratification (98.9% vs. 96.4% for OS, 100% vs. 98.5% for CSS). In multivariate analysis, however, overall mortailty was associated with older age (≥77 years, HR=1.501), concomitant diabetes (HR=2.293), and low risk stratification (HR=0.318), and PCa speficic mortality was solely associated with low risk stratification (HR=0.243), demonstrating no significant link between the implementation of RARP or RT.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that even the patient over 75 years old who could afford to undergo RARP for non-metastatic PCa had a similar survival in comparison with RT, regardless of risk stratification.
|
 |
|
keywords : mortality; radiation therapy; radical prostatectomy; robotic surgery |
|

