|
Cancer - Bladder, Pelvis, Ureter & Others(구연)
|
(E-057)
|
|
|
로봇 보조 근치적 방광 절제술 시행에 있어서 회장 도관 요로전환술 및 정위성 방광 조형술 시행 군 간의 삶의 질 비교 연구 |
| 인제대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실¹, 고려대학교 의과대학 비뇨기과학교실² |
| 김재윤¹, 조대연¹, 유지형¹, 성낙희¹, 정재용¹, 강석호² |
We aimed to compare quality-of-life (QoL) outcomes of patients who underwent ileal conduit (IC) urinary diversion with those who underwent orthotopic neobladder (ONB) reconstruction after robot assisted radical cystectomy (RARC) for invasive bladder cancers.
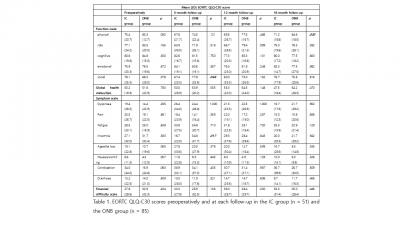
From November 2007 to December 2019, QoL outcomes of 136 patients underwent RARC and either IC urinary diversion or ONB reconstruction were evaluated. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) QoL questionnaire C30 version 3 was used to analyse QoL before surgery and 6, 12 and 18 months after surgery.
51 patients in the IC and 85 in the ONB group were included, totally 136 patients. The baseline characteristics did not showed significant difference between the groups..
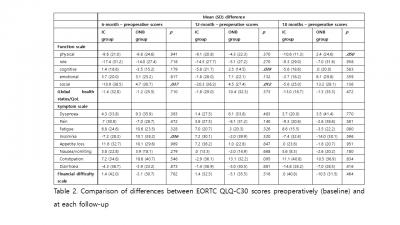
The social functioning (P = 0.048) and physical functioning (P = 0.020) was better in patients in the ONB group than in those in the IC group at 6, 18 months in the postoperative period, respectively. In addition the mean differences in social functioning from baseline to each follow-up at 6, 12 months were significantly different between the groups, with patients in the ONB group performing better (P = 0.037, P = 0.012, respectively). And the mean differences in physical functioning from baseline to follow-up at 18 months was significantly different between the groups, with patients in the ONB group performing better (P = 0.05).
RARC with ONB have better trend than IC in terms of physical functioning, social functioning, but insomnia may develop in short term. |
  |
|
keywords : bladder cancer, robot assisted radical cystectomy, quality of life |
|

